Private Repositories
JitPack supports building and installing from private Git repositories. Build artifacts are also kept private and you can only download them if you have access to the Git repository itself.
You can also share your build artifacts (jar, aar) publicly while keeping the source code private. For example, you can easily distribute your library to your users without giving them access to code.
A JitPack Subscription is tied to a specific GitHub/Bitbucket account which can be either a user or an organization. All repositories under that account can be built with JitPack and used by members of the organization.
Note that your GitHub organization may need to approve JitPack in order to access private repositories (Documentation).
Set up
To start using private repositories you will first need to grant JitPack access. Open https://jitpack.io/private and follow the steps:
-
Click Authorize to get your personal authentication token. Each member of your team should to get their own token.
-
Add the token to $HOME/.gradle/gradle.properties:
authToken=AUTHENTICATION_TOKEN -
Then use authToken as the username in your build.gradle:
repositories {
maven {
url "https://jitpack.io"
credentials { username authToken }
}
}
Maven setup
JitPack provides a private Maven repository that you can access with an authentication token.
Add the token to $HOME/.m2/settings.xml file:
<settings>
<servers>
<server>
<id>jitpack.io</id>
<username>AUTHENTICATION_TOKEN</username>
<password>.</password>
</server>
</servers>
</settings>
The id of the server must be the same you use in your pom.xml for JitPack.io.
Sbt setup
Create a new file $HOME/.sbt/.credentials and insert your authentication token:
realm=JitPack
host=jitpack.io
user=AUTHENTICATION_TOKEN
password=.
Then add this line to your build.sbt:
credentials += Credentials(Path.userHome / ".sbt" / ".credentials")
Note that the realm property in the credentials file is case sensitive and needs to be exactly JitPack.
Leiningen
Add the token to project.clj as the username:
:repositories [["jitpack" {:url"https://jitpack.io" :username "AUTHENTICATION_TOKEN" :password "."}]]
Bitbucket
To use JitPack with Bitbucket private repositories you need to create an App Password. The minimum scope that the password requires is Repositories: read. If you’d like to use Artifact Sharing then the required scope is Repositories: write.
In order to Look Up and manage Bitbucket repositories you should add the App Password to your JitPack account:
- Sign In on https://jitpack.io
- Click on your username (https://jitpack.io/w/user)
- Enter your Bitbucket user and App Password
Your user page also shows your access token that you should use in your build tool (Gradle/Maven/Sbt).
GitLab
To use JitPack with GitLab.com private repositories you need to create a Personal Access Token. The token requires read_repository and read_api scopes.
In order to Look Up and manage GitLab repositories you should add the Access Token to your JitPack account:
- Sign In on https://jitpack.io
- Click on your username (https://jitpack.io/w/user)
- Enter your GitLab Access Token
Your user page also shows your JitPack access token that you should use in your build tool (Gradle/Maven/Sbt).
If you are using a self-hosted instance of GitLab then you need to setup a Self hosted git server (see below).
GitLab Subgroups
To build a repository that is in a subgroup you can use a dependency in this form: com.gitlab.GROUP.SUBGROUP:REPO:VERSION
For example: https://jitpack.io/#com.gitlab.jitpack.test/gradle-lib
Usage
Once you are set up you can try installing one of your private repositories:
-
Go to https://jitpack.io/private and ‘Look up’ your private repository.
-
Follow the instructions and add credentials to your build file if using Gradle:
repositories {
maven {
url "https://jitpack.io"
credentials { username authToken }
}
}
Then add the dependency to your private repository just like you do with a public one:
dependencies {
compile 'com.github.User:PrivateRepo:Tag'
}
Azure
JitPack can build private and public git repositories from Azure DevOps (https://dev.azure.com). You can Look Up your project on jitpack.io using: com.azure.{Project}/{Repo}. For example: com.azure.jitpack/gradle-simple
To configure private repositories:
- Sign In on https://jitpack.io
- Click on your username (https://jitpack.io/w/user)
- In ‘Git server’ section enter https://dev.azure.com and then your Personal Access Token. The token should have Read&Write access to Code.
Private and transitive dependencies
Your private GitHub projects can have dependencies on other GitHub projects. JitPack supports resolution of these dependencies seamlessly and there’s no extra configuration required. The token you use to build the first project will also be used to build it’s dependencies.
For transitive dependencies to work in Gradle the authentication token property needs to be called authToken in all projects.
Permissions
Private repository builds are accessible to you and anyone who has Read permissions for the Git repository itself. For example, you may trigger a build of your library and your colleague will be able to install the library straight away.
Your private repository source code remains private.
Artifact sharing
There are two ways to share your build artifacts - public and private.
Artifact sharing publicly
In some cases you want to distribute your project publicly while keeping the source private. In this case:
- Sign In with a user that has push permissions
- Look up your private repository
- Click on the Settings icon
- Click on the Lock icon to make the builds public:
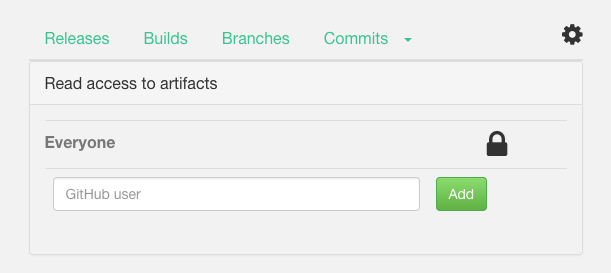
Once the Lock icon turns to unlocked the project’s build artifacts become public. That means your users will be able to install your library without needing an authentication token.
Artifact sharing privately
Anyone with read access to your Git repo can already download the build artifacts. You can also add additional collaborators on JitPack.io that will have read access to the build artifacts. They will not have access to the source code.
To add collaborators:
- Sign In with a user that has push permissions
- Look up your private repository
- Click on settings
- Add the collaborators GitHub username
Collaborators will need to sign in on JitPack.io to get their own authentication token.
Token based access
You can also generate additional tokens to access build artifacts, for example, if you want to download them from a CI. To generate a new token click ‘Generate’ in your repository’s settings. If you Generate a token again then the old one will be invalidated.
Custom domain
If your organisation’s GitHub url is https://github.com/yourcompany then by default the groupId of your artifacts will be ‘com.github.yourcompany’. If you want to use your own domain name as groupId, you can.
JitPack supports mapping your domain name to your GitHub organization. Then instead of ‘com.github.yourcompany’ groupId you can use ‘com.yourcompany’ while the name of the project and version remains the same.
To enable your own domain name:
-
Add a DNS TXT record that maps git.yourcompany.com to https://github.com/yourcompany
-
Go to https://jitpack.io/#com.yourcompany/yourrepo and click Look up. If DNS resolution worked then you should see a list of versions.
-
Select the version you want and click ‘Get it’ to see Maven/Gradle instructions.
Example: https://jitpack.io/#io.jitpack/gradle-simple
To check that the DNS TXT record was added run the command dig txt git.yourcompany.com. For example:
> dig txt git.jitpack.io
...
;; ANSWER SECTION:
git.jitpack.io. 600 IN TXT "https://github.com/jitpack"
Self hosted git
You can also use JitPack with a self-hosted Git server like GitLab or GitHub Enterprise. In that case, go to your user page and enter:
- Git server: https://gitlab.yourcompany.com
- Token: Personal Access Token (if using private repositories)
After that you’ll be able to access your libraries on the main JitPack page with:
- com.yourcompany.gitlab.USER/REPO
If you’d like to use a different groupId (as in com.yourcompany.USER/REPO) then you’ll need to setup a custom domain as described above. The only difference is that instead of GitHub point the TXT record to your git server. For example, if the address of your GitLab is https://gitlab.yourcompany.com then set the TXT record the following way:
- git.yourcompany.com points to https://gitlab.yourcompany.com
SSH Key Authentication
In addition to HTTPS JitPack also supports SSH key based authentication or Deploy Keys. You can generate keys on your user page and then add the public key to your Git repository.
If you would like to have admin permissions for the repository on JitPack then the deploy key needs to have push permissions.